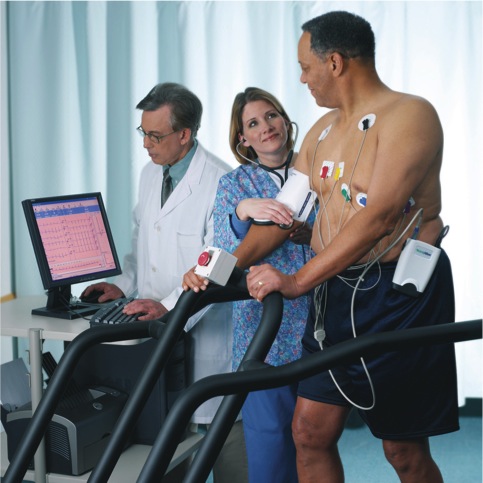
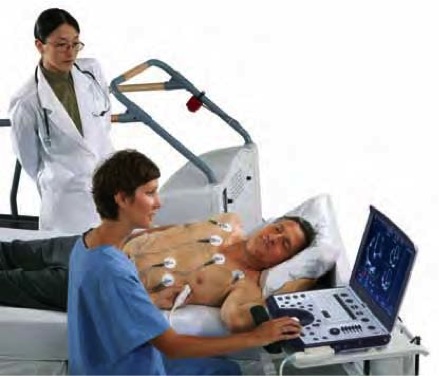
What is a Stress Test?
During a Stress Test, your blood pressure, heart rate and ECG are recorded continually to evaluate your heart’s response to exercise and to test for myocardial ischemia*. Stress testing with continuous ECG recording is a simple and frequently used screening tool for evaluating the likelihood of significant coronary artery disease. It is particularly useful when the resting ECG or Echo are normal.
What is the difference between PSE and DSE?
Additional imaging with echo improves the accuracy of the stress test. The stress test may utilize physiological or pharmacological exercise to stimulate the heart.
Physiological Stress Echo (PSE): Both ECG and Echo are recorded before, during and immediately after physiological exercise.
- Physiological exercise is performed on a treadmill with continuous ECG monitoring
- Echo is recorded at (1) rest (2) peak exercise and (3) recovery
- Contractility of left ventricular segments at rest and peak exercise is compared.
- Normal, hypokinetic and akinetic segments are noted.
PSE is a sensitive, specific and accurate method for detecting and localizing myocardial ischemia* or myocardial infarction* due to coronary artery disease. PSE is preferred to ECG stress test if the resting ECG is abnormal or when there is abnormal myocardial function on resting echo.
Dobutamine Stress Echo (DSE): Some patients are not able to exercise on a treadmill or bicycle due to disabilities or other medical conditions. In such patients, pharmacological stress may be performed in the supine (lying) position, whilst administering intravenous dobutamine.
- The ECG and Echo are recorded with increasing dosages of dobutamine.
- Contractility of left ventricular segments at rest and with increasing doses of dobutamine is compared.
- Normal, hypokinetic and akinetic segments are noted.
The Dobutamine Stress Echo is a useful method for detecting myocardial ischemia* and assessing myocardial viability* in patients with coronary artery disease. It is particularly useful for (1) patients who cannot undergo physiologic exercise on a treadmill and (2) for sedentary or patients confined to bed whose cardiac response to stress needs to be assessed before a surgical procedure (pre-op cardiac clearance).
*What is meant by myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction and viable myocardium?
- Myocardial ischemia refers to heart muscle (myocardium) that is not receiving adequate blood flow due to a narrowed coronary artery.
- Myocardial infarction refers to myocardium that has been damaged and scarred due to complete occlusion of a coronary artery.
- Viable myocardium (myocardial viability) refers to temporary and potentially reversible myocardial dysfunction due to severe ischemia. The myocardial dysfunction is likely to improve if the coronary artery flow is restored by angioplasty (PCI) or coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG).
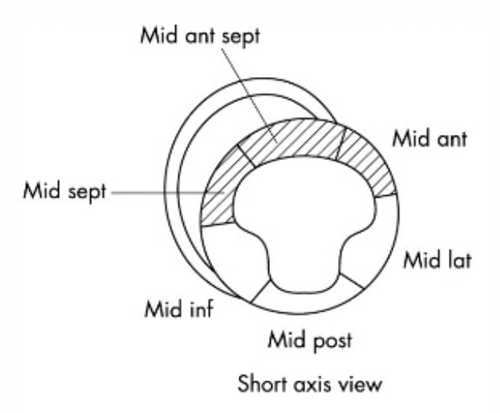
During a Physiological Stress Echo (PSE), how is left ventricular contractility at rest and exercise compared?
Normal contractility of all segments at rest
Increased contractility of all segments with exercise.
 |
|
This is a normal Physiological Stress Echo (PSE) study with increased contractility of all left ventricular segments during exercise. |