What is a Cardiac Arrhythmia?
An arrhythmia is an abnormal cardiac rhythm that may be either too fast, too slow, irregular or uncoordinated. This can result in palpitations, inefficient pumping of the heart, dizzy spells and blackouts. ECG and 24-hour Holter monitoring are useful in confirming the diagnosis.
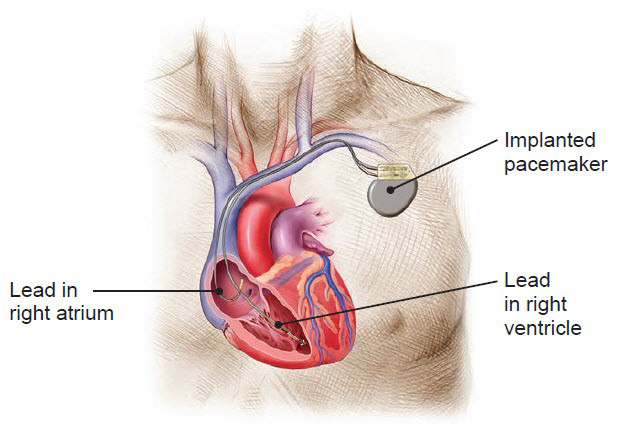
Bradycardia: A slow heart rate (bradycardia) may be due to complete heart block or sinoatrial node disease. Mild bradycardia may require no treatment. Severe bradycardia may require an implanted electrical device called a pacemaker for effective management.
Tachycardia: A rapid heart rate (tachycardia) may be due to ventricular tachycardia or supra-ventricular tachycardia. Severe tachycardia may require medical therapy to slow the heart rate or an implanted defibrillator to correct the rhythm when it goes too fast.
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular fast abnormal heart rhythm. Symptoms include palpitations, fatigue, breathlessness and dizziness. It may predispose to clot formation in the left atrium which may dislodge and cause a stroke. Medical therapy may be indicated to (1) control the heart rate (2) prevent the abnormal rhythm or (3) prevent clots from forming. In some cases the abnormal rhythm can be corrected by an electrophysiology ablation procedure.
What is a Pacemaker or Defibrillator Procedure?
These procedures are performed by a cardiologist, electrophysiologist or cardiac surgeon. The pacemaker or defibrillator device is implanted under local anesthesia in a Cardiac Catheterization Lab or Operating Theatre. The device is connected to a wire that passes through a vein into the heart. The device monitors and detects abnormally slow or fast heart rhythms and can send signals to pace a slow heart rhythm at an appropriate rate or convert an abnormally fast rhythm to the normal rate and rhythm.
What is a Cardiac Electrophysiology (EP) Study?
During a Cardiac Electrophysiology (EP) study, your Cardiac Electrophysiologist inserts catheters within the heart to map the electrical currents. This allows your cardiologist to better understand the way the electrical signals move through your heart. Ablation procedures can then be performed using heat or cold energy at the catheter tip to treat erratic electrical signals that cause an arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm). EP Studies and Ablation are performed in a Cardiac Catheterization Lab.